Generative AI could prove to be AI’s “iPhone moment” as its use cases reach the masses. In just a few months after launching, the number of visitors to ChatGPT had hit the one billion milestone. Generative AI tools have significantly boosted people's capability to comprehend context and swiftly produce content that closely resembles human output across various forms, unlocking boundless possibilities.
Because of this, businesses must act quickly and identify key generative AI use cases for their organisations before competitors steal a march on them. At a minimum, every knowledge worker’s productivity will be enhanced, while more future-looking use cases will see entire processes automated and decision making greatly augmented - AI-powered chatbots are the appetiser rather than the entrée. Firms must also balance the significant opportunities with the risks and uncertainty surrounding the outputs of generative AI.
Introduction
AI has already changed the way businesses work, but lingering doubts over AI’s ROI have never quite gone away. Yet the hype surrounding ChatGPT and other tools has led many to call generative AI a paradigm shift in the history of AI.
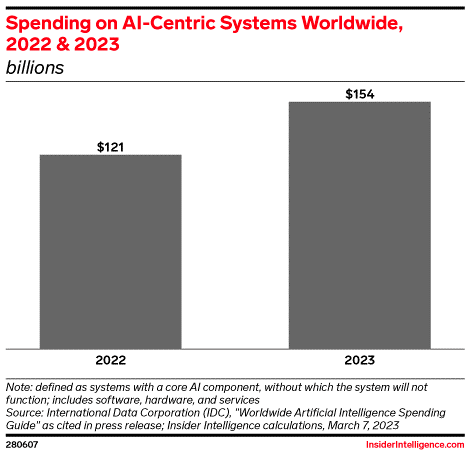
Businesses are bullish on the impact of AI. The spending worldwide on Global AI is estimated to surge by over $30 billion to $154 billion in 2023. Generative AI can finally deliver much of AI and machine learning’s highly purported benefits, including better decision making, enhanced customer service, and back-office efficiencies.
So why is this AI’s moment? How can generative AI change financial services and be applied across key business areas?
In this blog we unpack how generative AI works in practice, how firms are currently using it, and how they might do in the future.
What Is Generative AI?
Generative AI is a type of AI that can create entirely new content that resembles human-generated content. This includes text, audio, images, and video. Current generative AI tools scour data largely from the public domain that is within their training period.
Large language models (LLMs) are at the core of generative AI tool's capabilities, and rely on deep learning algorithms called transformers to create outputs similar to human content. Transformers are a subset of machine learning designed for natural language processing and other tasks. Significant improvement in language-related tasks has been achieved by utilising self-attention to grasp word context and relationships.
A number of recent technological breakthroughs have greatly enhanced generative AI:
- LLMs: A type of AI that trains models on huge datasets using deep learning techniques to understand human language and generate similar content. The cost to train a large language model to GPT-3 level performance collapsed from $4.6 million in 2020 to $450,000 in 2022 and will continue declining at 70% YOY through to 2030.
- Transformers: Machine learning models that break down text into smaller groupings while processing them. This allows models to be trained on expanding datasets without needing to label data in advance by enabling models to understand the context of each word and sentence in relation to wider context.
- Generative adversarial networks (GANs): A key approach behind generative AI tools that allows models to continuously improve content generation. Two neural networks work in parallel to generate content while the other works as an editor, evaluating the answers.
How Does It Work?
Users prompt generative AI tools with an input that could be plain language, an image, or a video. The tool then responds with an answer that matches the prompt. Behind this rapid generation of content, however, is a process with multiple steps. Let’s take the example of a text prompt for ChatGPT.
Firstly, the input is converted from words to an illustrative set of numbers that can be processed. Next, the characters – or “tokens” – that make up the input are defined. LLMs can then connect the components – the words, grammar, and context – of the input using its attention network. Through billions of training runs the model understands the language. Building comprehension, the LLM can then create a response one word at a time, taking the previous word(s) into account.
This is called hallucination. One thing to bear in mind is that transformers are just a model that provide an advanced auto-complete functionality. In that sense they are not trying to answer your question but rather to find the words that come after your words. Depending on the way they are configured and the way you’ve phrased the prompts, those next words might very convincingly provide you with utter nonsense.
Why Is This Different To Previous AI Tools?
Generative AI combines human and ‘super-human’ capabilities. Two key human-like capabilities of generative AI have led many to label this as a breakthrough moment. Firstly, its language comprehension: its tools understand the context of prompts and the intent behind them. Secondly, its output resembles human-like content. Combined with its machine-powered ability to combine vast sources of data and recognise patterns at scale, its potential is transformative. Add in incredible advances in speech-to-text and text-to-speech, and generative AI will quickly become an indispensable piece of technology for global businesses.
The consequence of this will potentially greatly boost workforce output. Western countries – with the UK a prime culprit – have suffered from a productivity decline over the past decade, and this could inject life into flagging workforces. The widespread adoption of generative AI technologies is a breakthrough moment as AI applications reach the masses.
Currently, ChatGPT and other tools largely only have access to information in the public domain – but once private, proprietary data is incorporated into models, the use cases will expand. More so, customisable GPT models that can be trained on an organisation’s own data will drive cost savings across the business through automation, while improving decision making.
What Are The Opportunities For Financial Services Firms?
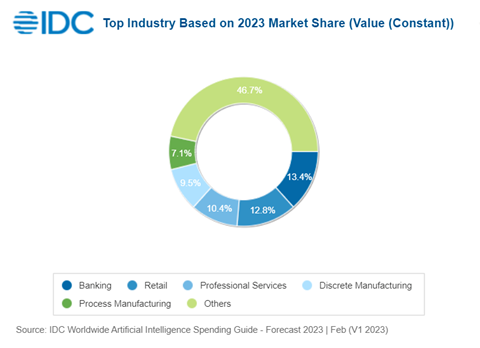
LLMs will make the long-heralded benefits of machine learning and AI a reality by unlocking a series of use cases that will provide a better customer service, augmented decision making, and deliver efficiency gains. Banks and retailers will make the largest AI investments in 2023, per IDC.
Enhanced Customer Experience
Generative AI has the potential to vastly improve customer experience with on-demand support and personalised advice - and Chatbots will take conversational finance to the next level. Existing chatbots rarely give users the feel that they are dealing with a human assistant – for better or worse – and can only handle simple queries. LLMs can better decipher context and intent to generate human-like responses, and customers will get quicker and more accurate answers. They will also be able to direct the AI to complete tasks, such as scheduling payments.
During this time, the LLMs will be learning more about each customer. Combined with enhanced customer insights, generative AI will offer tailored financial advice and hyper-personalised recommendations based on the individual customer’s unique situation. For example, fintech Brex is collaborating with OpenAI to roll out chat-powered spend insights and benchmarks for customers.
Scaling Data Analysis and Insights
Generative AI will put more accurate and plentiful data at the fingertips of knowledge workers. A wider range of information can be incorporated into training data to scale analysis and generate deeper insights. Capital markets firms will greatly enhance their investment strategies and ability to generate alpha by scaling the speed and depth of their market research. Firms will supplement more traditional research with sentiment analysis from the latest news and commentary and other alternative sources. This will supercharge existing capabilities to create customised charts on the fly enabled by natural language query. For example, leading hedge fund Citadel is said to be in discussions with OpenAI to leverage ChatGPT to generate insights across its entire business.
Fraud Detection and Prevention
Generative AI will also greatly enhance the ability of financial services firms to proactively identify fraudulent activity. A key differentiator is that generative AI can produce synthetic training data to train machine learning models with more abundant and relevant data. Machine learning models analyse transaction data to more accurately and effectively detect fraud. This will enhance key risk processes, such as anti-money laundering.
Mass Digitisation Automation
In the nearer term, arguably the true value creation of generative AI will be the boost to productivity. AI will take over mundane tasks such as data entry, and workers' hours spent trawling inefficiently for information will be cut. Zurich is simplifying long and complex claims documents using a tailored version of ChatGPT, for example. Key labour-intensive processes that require a high degree of accuracy will become more efficient, such as creating financial reports and other repetitive functions like creating contracts.
Generative AI could also be a gamechanger in software engineering. In the nearer-term, LLMs are already acting as coding assistants that can help developers produce a chunk of their code. Software engineers can use LLMs to accelerate development and the debugging of software. Use cases include writing pseudo code, unit tests, and debugging historical code. Going forward, LLMs should be able to code on the fly by translating language into code.
What Are The Current Limitations?
There are a number of challenges and risks that businesses must consider when leveraging generative AI that stem from inaccuracy and explainability limitations.
Explainability
Currently there is zero understanding about how GPTs produce their answers. Generative AI chatbots create content by generating a series of predictions on the statistically likely ‘token’ that comes next. Synthetic training data generated by AI is even harder to explain. Businesses need to be able to take accountability for these decisions or they will fall foul of regulators. The ethical and appropriate use of AI is a key area of focus for regulators, like the FCA, and firms will need to make sure they are ahead of future regulations.
Inaccurate Information
It is well-documented now that ChatGPT has no notion of truth. It creates content based on available data and poor quality inputs will generate poor quality outputs. What’s more, ChatGPT mostly responds to questions with a high level of assuredness that makes it near impossible to know when its answers are inaccurate. This creates a reliability problem for businesses if they make critical decisions based on inferior quality information and the assumption that a clever AI will be right. In the business world this could have vast repercussions, such as incorrectly rejecting loan applications.
This risk can be mitigated by providing generative AI tools with the right prompts and guardrails. This could include appending guidelines such as “only answer questions for which you know the answer to be true” and embedding in the workspace itself “only answers questions about XYZ topics.”
Data Privacy
Giving generative AI technology access to more private, proprietary data also creates significant data privacy risks. ChatGPT believes it owns all the data that it has access to; while this hasn’t proved troublesome so far with publicly available data, once the AIs are fed customer data, firms must be careful to comply with strict data privacy laws (GDPR).
BJSS, however, uses Azure OpenAI, where your data remains your own and does not become part of OpenAI GPT training data. This gives clients assurance that they’ll be supported and will avoid any potential legal issues.
Societal Fall-Out
The perceived risks stemming from the wider use and applications of AI led over 1,000 AI leaders to sign an open letter calling for AI labs to hit pause on AI research for six months. As AI’s far-reaching impact to everyday life becomes a reality, key signatories like Steve Wozniak have called for the world to take stock on how we want to put generative AI to use, halting training of AI systems more powerful that GPT-4 before it is too late. But this would be unenforceable in reality and new regulation that forces disclosures on how systems are trained should instead become a priority.
In an era of “fake news,” this ramps up the risks of the contagion of misinformation. And scaling bad decision making that is based on bias is also a scarily realistic possibility. Humans will remain critical in the application of generative AI to verify and appraise the outputs... for now.
Forward Looking Summary
Despite current limitations and related risks and challenges, the business world will soon be split between those that leverage the power of generative AI and those that don’t. Over 80% of banks believe that unlocking value from AI will be the key differentiator between winners and losers. The rapid development of generative AI is exciting and scary in equal parts: ChatGPT-4 can produce a short story's worth of content in one go now, compared to ChatGPT-3's limitation of a long article. Equally the opportunity for mundane tasks to be automated must be balanced with the threat to historically low employment levels.
How BJSS Can Help?
With extensive experience and expertise, BJSS is a top UK technology and business consultancy, renowned for its collaboration with financial services firms. Its aim is to help these organisations become data-driven while efficiently managing data privacy risks and meeting regulatory requirements.
BJSS is also a proud to announce that it has been chosen by Microsoft to join its OpenAI Accelerator Programme – a UK initiative that aims to support the adoption of innovative and fast-moving Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies and solutions.
Click here to learn more about the services we offer.
Published
April 29, 2024Reading time
7 minutesRelated posts